A salaried musician is an employee who earns wages or a salary for performing music services for an employer such as an orchestra, band, theatre company, or recording studio rather than working independently as a self-employed artist. Quebec has similar rules to the CRA for salaried musicians, with specific forms for claiming deductions.
If a taxpayer is required to provide his or her own instrument during the year, the expenses associated with the use of the instrument can be deducted. The deduction claimed for such expenses cannot exceed the income earned from employment as a musician in the year. A salaried musician can deduct allowable employment-related expenses such as:
- Maintenance costs
- Rental fees
- Insurance premiums
- Capital Cost Allowance (CCA) if they own the instrument
If you use your musical instrument for employment, self-employment, and personal purposes, you must allocate the total expenses between these uses. Only the employment-related portion is deductible — personal use is not.
Artist Expenses:
Expenses may be deducted for earning employment income from artistic activities if composed, performed, created, or participated in certified professional artistic work, excluding reproductions.Example :
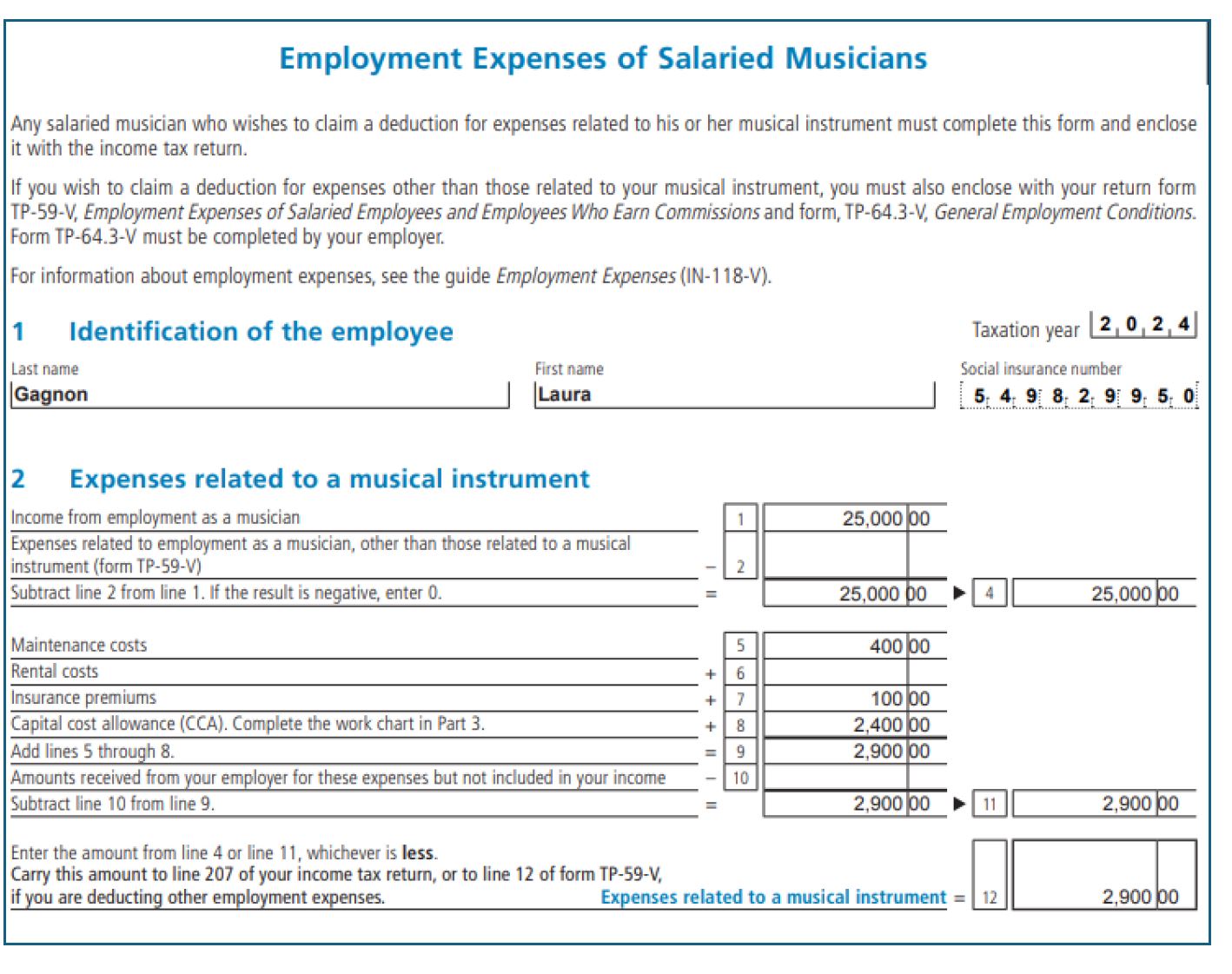
Salaried Musician: Laura, a violinist, earned $25,000 from artistic employment, spent $150 on strings, $100 on insurance, $250 on repairs, $500 on advertising, and bought a $12,000 violin (Class 8, 20% CCA rate)
Answer: Advertising expense can only be claimed by Commission employees.
Step 1: Musical instrument deduction: $500 + $2,400 (CCA) = $2,900
Step 2: Total employment expense = $2,900
Line 22900 = $2,900
Line 207 = $2,900
Example :
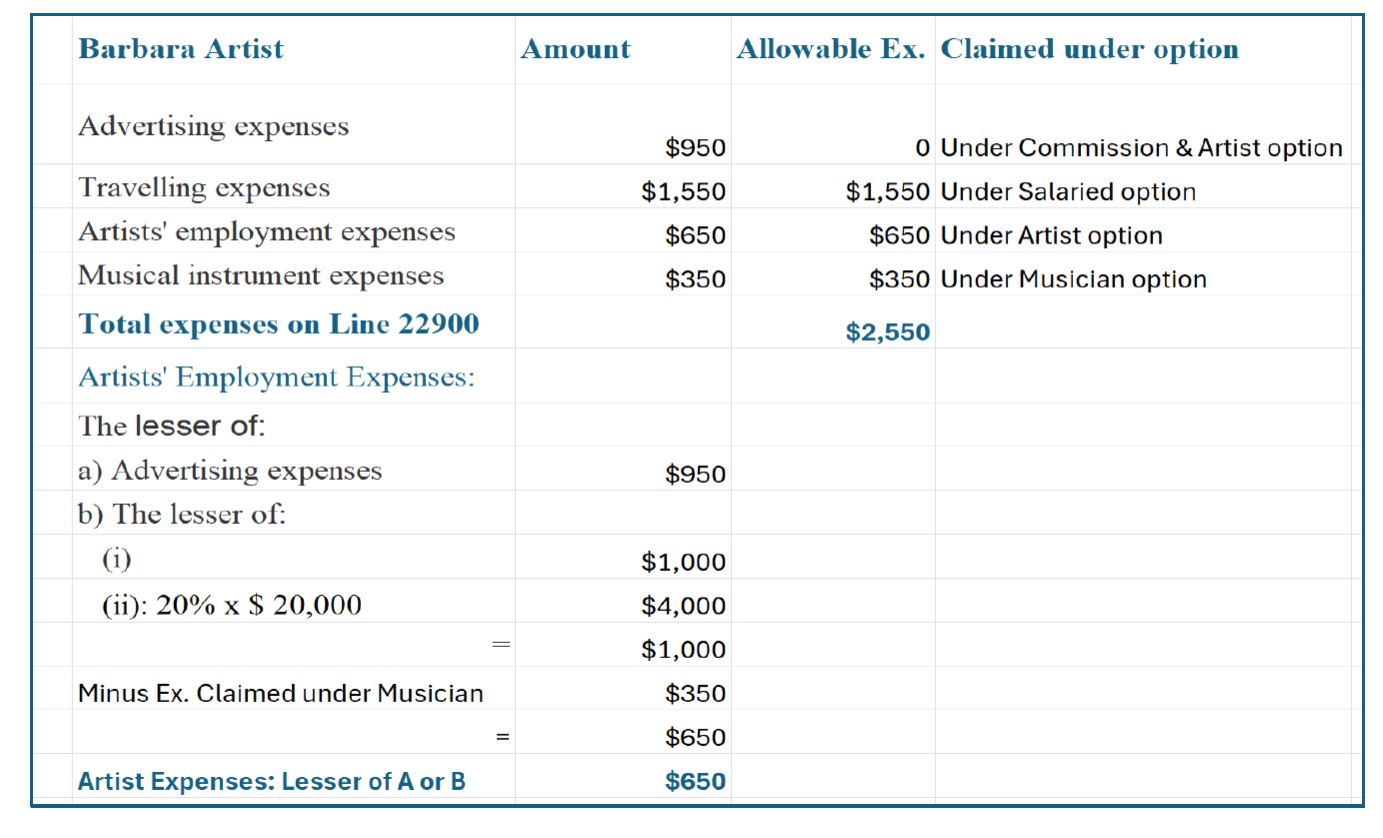
Barbara, a salaried artist earning $20,000, incurred $950 for advertising, $1,550 for travel, and $350 for musical instrument expenses.
Answer:
Salaried Musician Expenses: Federal vs Québec
| Expense Type | Federal (CRA) | Québec (Revenu Québec) |
|---|---|---|
| Musical Instruments & Supplies | Deduct the cost of instruments, strings, sheet music, and other work-related supplies. Capital cost allowance (CCA) may apply for instruments. | Same; reported on Form TP-59-V with employer certification on TP-64.3-V. |
| Home Office Expenses | Portion of utilities, rent, maintenance, and certain home insurance and property taxes if used for work. | Same rules; claimed on TP-59-V. |
| Travel & Vehicle Expenses | Deduct travel for performances away from the regular workplace; commuting is not deductible. Vehicle CCA, fuel, insurance, and maintenance can be included. | Same rules; claimed on TP-59-V. |
| Professional Fees & Dues | Memberships, union dues, or licensing fees required by the employer are deductible. | Same; professional dues reported on TP-59-V. |
| Training & Development | Courses to maintain or improve musical skills required for employment are deductible. | Same; must relate directly to employment skills. |
Posted on 8 January, 2026